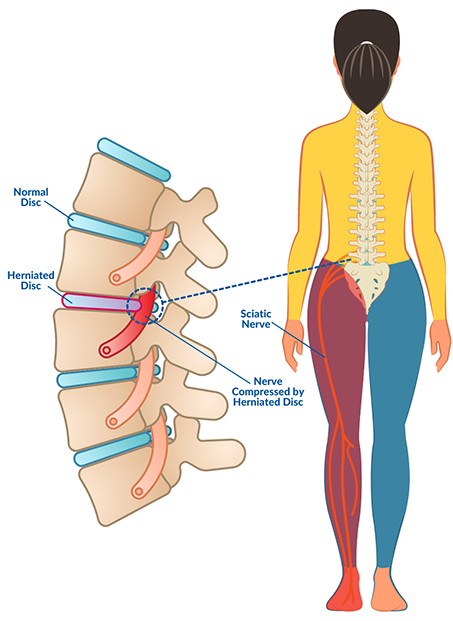
Herniated discs can be debilitating, causing pain, numbness, and varying degrees of discomfort. This condition can also lead to chronic pain and a high risk of developing chronic disease. People who suffer from herniated discs are often in constant pain and need to seek medical attention. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available. Depending on the stage of the disease, you may experience any one or a combination of these.
Herniated discs are most commonly caused by aging. The disks in the spine are thin and brittle, and wear over time can cause them to rupture. When this happens, the disk presses on the spinal nerve, causing significant pain. The best treatment is to consult a physician for an evaluation. Your doctor can prescribe pain medications that are effective for a short period of time. Your doctor may recommend surgery if your symptoms do not improve within three months.
There are many treatments for herniated discs, including physical therapy and medication. Your doctor will likely prescribe an acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug to help you manage your pain. If you do not improve after the pain medicine, you may need surgery. If the condition has not healed, you may be able to do exercises. However, if you are unable to do these exercises, you should consult a medical professional.
The main treatment for herniated disc is rest. The pain will usually improve after a few days, but you may require medication to relieve the pain. You should consult your doctor before making a decision. Most herniated discs do not require surgery. After the surgery, you should expect to be back to normal within three weeks. In some cases, you will no longer need any medication. This will reduce your chances of chronic pain in the future.
X-ray examination is the most common procedure for herniated discs. x-rays can reveal a herniated disc. CT is an MRI that can show calcified discs. Computed tomography has some limitations, but it is more convenient than MRI. Although MRI is the procedure of choice for herniated discs, it does not show herniated discs in the early stages.
In many cases, herniated discs are minor and do not pose a serious problem. The only symptom is pain and numbness. Some people may experience tingling or numbness, as well as compression of the spinal nerves. If a herniated disc is causing pain, rest and medication are your best options. You may need to undergo surgery to repair the damage. The site medicosencampeche.com.mx
says that if you have a severe herniated disc, you may need physical therapy or medication to relieve pain.
Discs are cushion-like cushions between the vertebrae. If a disc herniation is severely damaged, it can irritate the nerve roots. You may have to stay in bed for three months to avoid causing more damage. In some cases, you may be cured without an epidural steroid injection. The best treatment option for a herniated disc is physical therapy.
A doctor may recommend physical therapy or prescription medication for your condition. Your doctor will perform x-rays to identify structural instability. If your doctor finds a fracture, he or she may order an MRI or CT scan. A CT scan can show the herniated disc if it has calcification. A herniated disc is often a symptom of an unmanageable spinal disorder.
While herniated discs are common in people who are overweight, a herniated disc is not always a life-threatening condition. Most of the time, the damaged disc is only a small portion of the affected area. It is important to avoid bending over, lifting, or twisting the spine. This type of herniated disc can lead to a lot of pain and disability. Your doctor should be able to prescribe the right type of treatment.
A straight leg raise test is a good predictor of a herniated disc in people under 35 years of age. This test involves bending the affected leg while keeping it straight. If a person experiences pain in the leg or below the knee, they may have a herniated disc. A MRI scan is another option for determining a herniated disc. If a patient has back pain, an MRI will determine the affected vertebra.